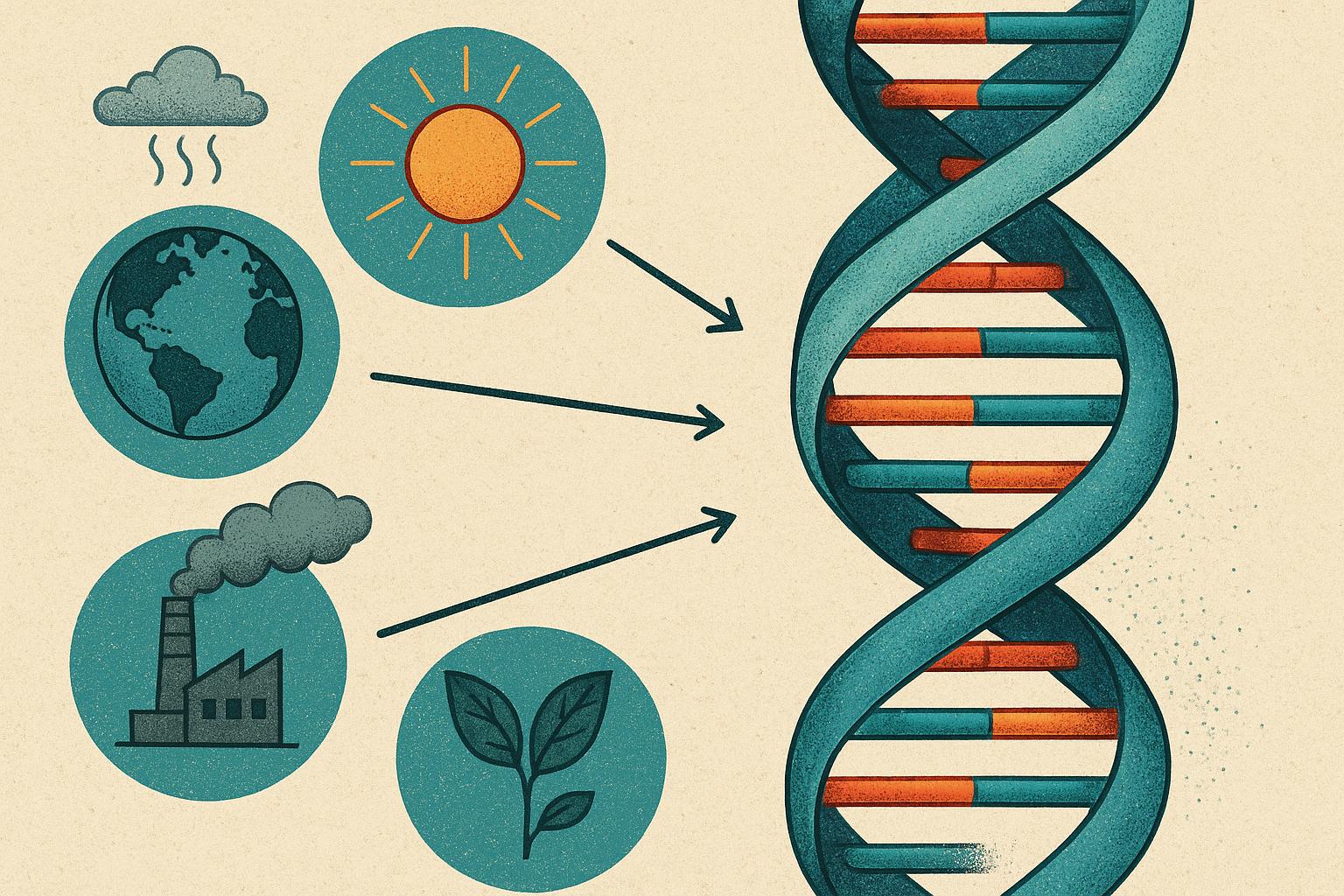
Environmental factors are known to have significant impacts on DNA, influencing both the structure and function of our genetic material. Understanding these interactions is pivotal in the study of genetics, disease, and evolution. This article delves into how various external elements affect DNA and the implications for human health.
The Role of Environmental Factors in DNA Alteration
Environmental influences on DNA are diverse and expansive. The primary pathways through which these factors induce alterations include direct interactions with DNA strands or the triggering of internal mechanisms leading to genetic expression modifications. With the expansion of human development and technological progress, individuals are increasingly exposed to numerous environmental factors that contribute to genetic changes. Among these, pollution, ultraviolet (UV) radiation, diet, and smoking hold substantial weight.
Pollution and DNA Integrity
Pollution, particularly air pollution resulting from industrial activity and vehicle emissions, presents a significant threat to DNA integrity. Pollutants such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) can penetrate biological systems. These chemical compounds have a high affinity for DNA, forming adducts within the DNA strands, leading to potential structural mutations. The mutagenic effects of PAHs and similar pollutants are associated with a heightened risk of cancer and other genetic disorders. Research indicates that sustained exposure to these harmful substances can overwhelm the body’s natural defense and repair mechanisms, leading to more permanent genetic alterations.
Ultraviolet Radiation
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is a well-known environmental factor impacting DNA. The sun emits UV rays, which, during prolonged exposure, can induce thymine dimers in DNA sequences. These dimers are an abnormal linkage between two adjacent thymine bases on a DNA strand. This abnormality can disrupt DNA’s normal functions, such as replication and transcription. An inability to repair these irregular structures may give rise to mutations, contributing to the development of skin cancer types, including melanoma. The risk associated with UV radiation accentuates the need for protective measures, such as sunscreen and clothing, to minimize skin exposure.
Dietary Influences on DNA
Diet is a fundamental factor in DNA maintenance and repair. Nutritional choices influence the level of oxidative stress within the body, with antioxidants playing a protective role against DNA damage. Consuming a diet rich in fresh fruits and vegetables introduces antioxidants capable of neutralizing free radicals and reducing oxidative stress. Conversely, diets heavily reliant on processed foods can lack essential nutrients, exacerbating DNA damage and impairing the body’s natural repair processes. Furthermore, diet affects epigenetic markers, which are critical in gene expression regulation. The relationship between diet and epigenetics underscores the importance of balanced nutrition for maintaining DNA health (source).
Impact of Smoking
Smoking is another significant factor that compromises DNA integrity. Tobacco smoke is laden with numerous carcinogenic compounds known to interact adversely with DNA. These interactions frequently culminate in DNA adduct formation, where carcinogenic chemicals bind to DNA, leading to structural modifications and potentially triggering mutations. The mutagenic nature of these interactions elevates the risk of cancer, particularly in tissues directly exposed to smoke, such as lung tissue. Additionally, smoking can contribute to systemic health issues by inducing genetic changes that affect various organs and bodily functions.
Mechanisms of DNA Repair
The human body possesses remarkable mechanisms to counteract environmental DNA damage. These include nucleotide excision repair, base excision repair, and double-strand break repair, which serve as corrective processes for various types of DNA damage. Nucleotide excision repair is particularly effective against bulky DNA adducts, while base excision repair targets modified bases. Double-strand break repair mends disruptions across both DNA strands. These repair pathways underscore the inherent resilience of biological systems in mitigating potentially hazardous environmental impacts.
However, these mechanisms are not infallible. The efficiency of DNA repair can be compromised when repair pathways are overwhelmed by excessive damage or when inherent defects exist in the repair enzymes themselves. In such scenarios, unrepaired DNA damage can lead to permanent mutations, increasing susceptibility to cancer and other genetic conditions. Understanding and enhancing these repair mechanisms remains a key focus in biomedical research and therapeutic development.
Conclusion
The complex and ongoing interaction between environmental factors and DNA is crucial for the fields of genetics and public health. Exploring how external elements such as pollution, UV radiation, dietary habits, and smoking contribute to DNA alterations is vital for advancing medical research and implementing effective public health initiatives. While DNA is constantly under the influence of various external factors, the robust nature of biological repair systems illustrates the potential for minimizing genetic damage. Nonetheless, proactive measures to reduce exposure to harmful environmental influences are essential in preserving DNA integrity and promoting long-term health outcomes.
Overall, mitigating the impact of environmental factors on DNA requires a combination of personal responsibility and broader societal interventions. These include policy measures targeting emissions reductions, public education on the dangers of excessive sun exposure, promoting balanced dietary guidelines, and smoking cessation programs. Continued research and collaboration among scientific, medical, and policy-making communities will be instrumental in safeguarding human genetic health against the backdrop of environmental challenges.